The following scenarios are provided from help service offered to actual customers.
It means that the disk's space for the partition you are trying to recover is occupied by another existing parition(s). It also means that you are either trying to recover an improper partition, or, if you are 100% sure that it is your lost partition - the existing partition located underneath the Hard Drive device is invalid (for example, you deleted original partition and re-created a new one instead).
Verify that the partition you are trying to recover is an original one and actually contains your data. If so, proceed to the step 2.
Verify that the existing partition(s) that overlaps with the one you are trying to recover is invalid. If so, you need to delete the existing invalid partition(s) using either the Computer Management console, or execute Delete Invalid Partition command from Tools menu.
Find and try to recover your original partition once again.
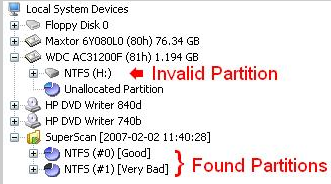
Note: Selecting, File -> Save Scan Results can save time and avoid having to re-scan the hard drive.
It means that partition table is full and there is no space there to insert a recovered one. Standard partition table can contain only 4 partitions including one extended.
Verify that partition you are trying to recover is an original one and actually contains your data. If so, proceed to the step 2.
Verify existing partition(s). Find out invalid one or not needed ones and delete them using either Computer Management panel, or execute Delete Invalid Partition command form Tools.
Find and try to recover your original partition once again.
It means that file system on the partition being recovered is not supported (i.e. Linux Ext2fs, etc...) or file system itself is invalid. Partition Recovery is unable to recover such partitions.
It means that partition has been is written back to the partition table, but we are unable to verify the results. Windows does not let the software to refresh volumes.
It could also mean that drive letter cannot be assigned for some reason.
Try to reboot the machine and verify the results.
It means that you are trying to restore Extended partition and another partition of type Extended already exists on the disk. Only one extended partition is allowed to reside on the disk.
It means that underlaying file system is damaged on the partition being restored. In spite the fact that partition recovery software corrected MBR, Partition Table and Boot Sectors - something else within file system is damaged (or overwritten) on the recovered drive, for example - MFT records on NTFS, Root or FAT areas on FAT. As long as disk integrity test is not passed, Windows displays such a message.
It could happen in case if you've recovered not a proper partition or in case if file system is actually damaged.
I successfully restored all my volume data to another USB disk (all-at-once option). When I plug this USB to another PC, Windows pops up 'Access denied' error and my data not accessible. Why this happens and what to do?
Most likely this is a Windows security issue, so this recovered volume has been created under Windows user account that has not been registered (or doesn't have enough rights) at the PC where you plugged in your USB. You need to log on as an Administrator and assign proper rights for the volume to be accessed.
Here is a video how you can do it.
This document is available in PDF format,
which requires Adobe® Acrobat® Reader
(Free download):